Heat-conducting plastic could lead to lighter electronics, cars
Unfurling the long chains of molecules in plastics could help them dissipate heat more easily.

Unfurling the long chains of molecules in plastics could help them dissipate heat more easily.
Advanced plastics could usher in lighter, cheaper, more energy efficient product components, including those used in vehicles, LEDs and computers—if only they were better at dissipating heat. A new technique that can change plastic’s molecular structure to help it cast off heat is a promising step in that direction.

Developed by a team of University of Michigan materials science and mechanical engineering researchers and detailed in a new paper published today in Science Advances, the process is inexpensive and scalable, and the concept can likely be adapted to a variety of other plastics. In preliminary tests, it made a polymer about as thermally conductive as glass—still far less so than metals or ceramics, but six times better at dissipating heat than the same polymer without the treatment.
“Plastics are replacing metals and ceramics in many places, but they’re such poor heat conductors that nobody even considers them for applications that require heat to be dissipated efficiently,” said Jinsang Kim, a U-M materials science professor and an author on the paper. “We’re working to change that by applying thermal engineering to plastics in a way that hasn’t been done before.”
The process is a major departure from previous approaches, which have focused on adding metallic or ceramic fillers to plastics. This has met with limited success; a large amount of fillers must be added, which is expensive and can change the properties of the plastic in undesirable ways. Instead, the new technique uses a process that engineers the structure of the material itself.
Plastics are made of long chains of molecules that are tightly coiled and tangled together like a bowl of spaghetti. As heat travels through the material, it must travel along and between these chains—an arduous, roundabout journey that impedes its progress.
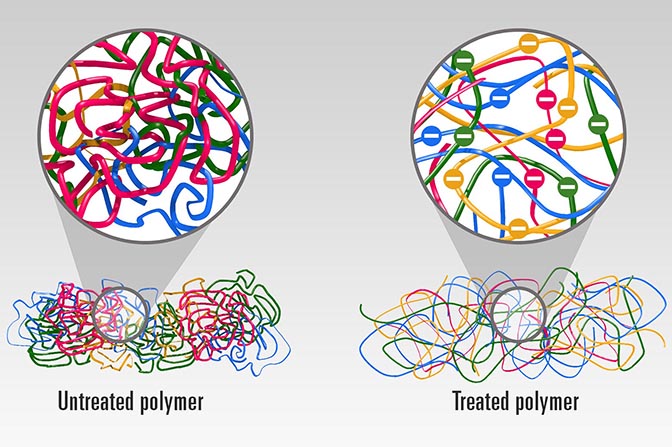
The team, which also included U-M associate professor of mechanical engineering Kevin Pipe, mechanical engineering graduate researcher Chen Li and materials science and engineering graduate student Apoorv Shanker, used a chemical process to expand and straighten the molecule chains, giving heat energy a more direct route through the material. To accomplish this, they started with a typical polymer—or plastic. They first dissolved the polymer in water, then added electrolytes to the solution to raise its pH, making it alkaline.
The individual links in the polymer chain—called monomers—take on a negative charge, which causes them to repel each other. As they spread apart, they unfurl the chain’s tight coils. Finally, the water and polymer solution is sprayed onto plates using a common industrial process called spin casting, which reconstitutes it into a solid plastic film.
The uncoiled molecule chains within the plastic make it easier for heat to travel through it. The team also found that the process has a secondary benefit—it stiffens the polymer chains and helps them pack together more tightly, making them even more thermally conductive.
“Polymer molecules conduct heat by vibrating, and a stiffer molecule chain can vibrate more easily,” explains Shanker. “Think of a tightly stretched guitar string compared to a loosely coiled piece of twine. The guitar string will vibrate when plucked, the twine won’t. Polymer molecule chains behave in a similar way.”

Pipe says that the work can have important consequences because of the large number of polymer applications in which temperature is important.
“Researchers have long studied ways to modify the molecular structure of polymers to engineer their mechanical, optical, or electronic properties, but very few studies have examined molecular design approaches to engineer their thermal properties,” Pipe said. “While heat flow in materials is often a complex process, even small improvements in the thermal conductivities of polymers can have a large technological impact.”
The team is now looking at making composites that combine the new technique with several other heat dissipating strategies to further increase thermal conductivity. They’re also working to apply the concept to other types of polymers beyond those used in this research. A commercial product is likely several years away.
“We’re looking at using organic solvents to apply this technique to non- water soluble polymers,” said Li. “But we believe that the concept of using electrolytes to thermally engineer polymers is a versatile idea that will apply across many other materials.”
The paper is titled “High thermal conductivity in electrostatically engineered amorphous polymers.”